Langfuse
I also explored Langfuse as an alternative to LangSmith, specifically the local host option, Self-host > Local (docker compose).
Pre-requisite and setup
- Getting started was easy. However, the default port used in localhost is port
3000, which has been occupied in my case. Therefore, I modifieddocker-compose.ymlto map toward another local port, e.g.3030. Then again,docker compose up.
ports:
- "3030:3000"
- Now, we can access Langfuse at
http://localhost:3030instead.
- You’d see the below screen and can click sign-up to setup a user account for local usage.
- After setting up an account and a project, here are some screenshots over the interface of langfuse and how you can go ahead and setup API keys for local dev usage.

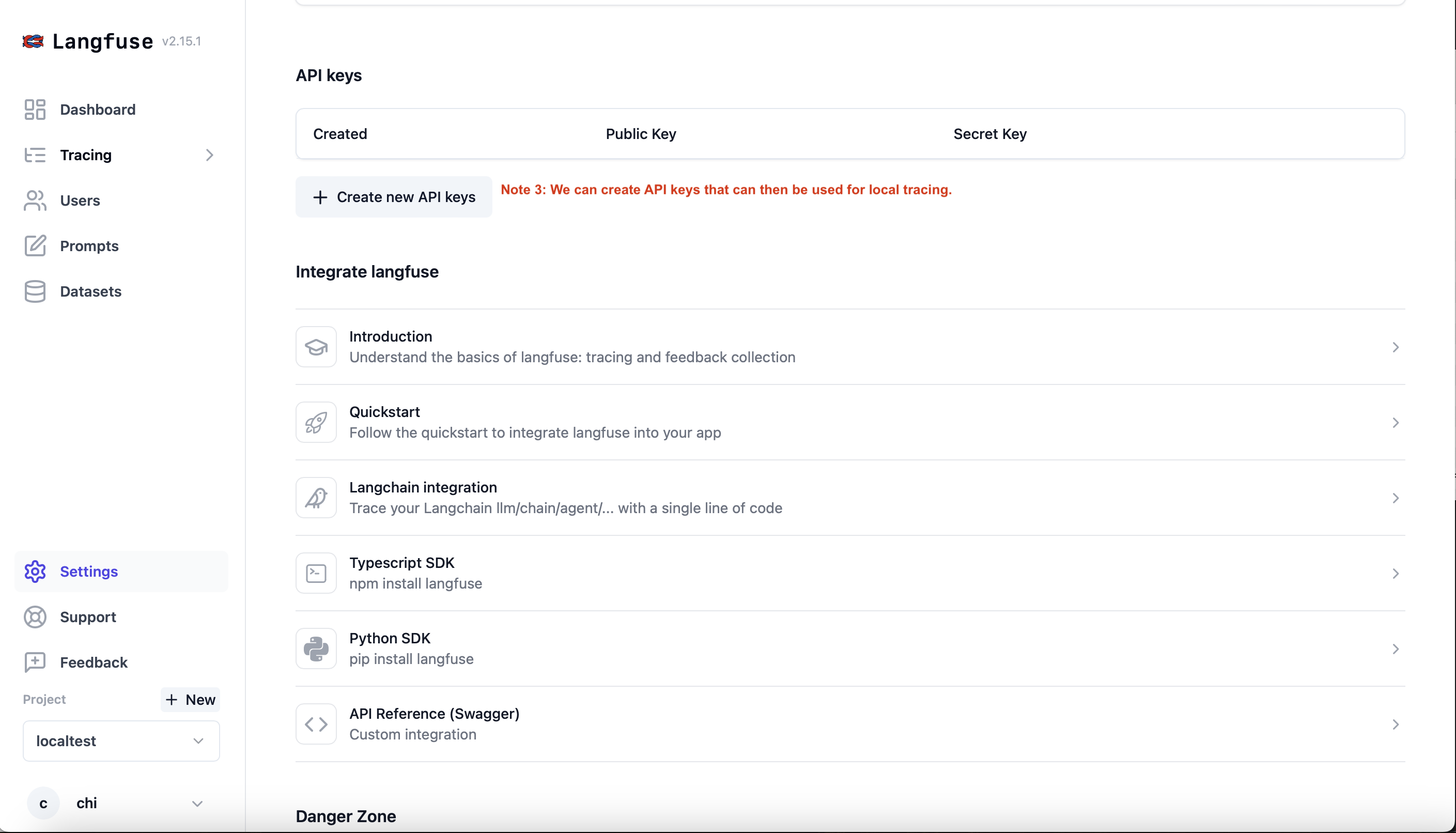
- Now that we have created the API keys, we just need to add
LANGFUSE_HOST,LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY,LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEYas environment variables and we’re ready to leverage langfuse.
If you’re using Langchain
-
No additional specification is needed once the environment variables are all set other than to import associated langfuse modules.
-
For example, I made the followin example: Using the Chatllama agent using local llama2 docker image and Langchain:
# Import packages
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langfuse import Langfuse
from langfuse.callback import CallbackHandler
# Setup Chatllama agent
llm = ChatOllama(model="llama2")
# Setup Prompt template
text = "You are a travel agent that help people prepare travel itinerary. {question}"
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(text)
# Chain
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# Langfuse configuration to create Prompt logging
langfuse = Langfuse()
langfuse.create_prompt(
name="ollama-test-prompt",
prompt=text,
is_active=True,
config = {
"model": "llama2",
"temperature": 0.2,
"supported_languages": ["en"]
}
)
# Langfuse callback handler to allow traces
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler(
session_id="test-1234",
user_id = "chi-local"
)
# Invoke the chain to answer the user question
print(chain.invoke({"question": "Travel plan for 6 days Iceland travel in June."},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}))
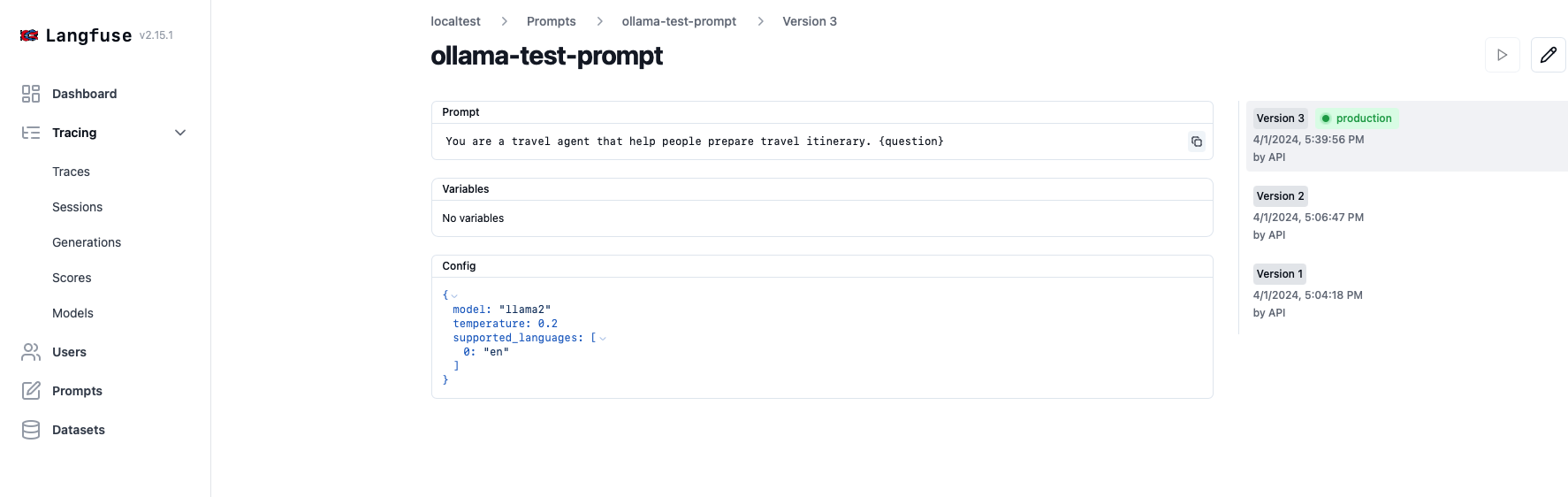
- We’d found the running under the
localtestproject.As we have specifiedlangfuse.create_promptconfigurations, the prompt template and model config is logged underPrompts:
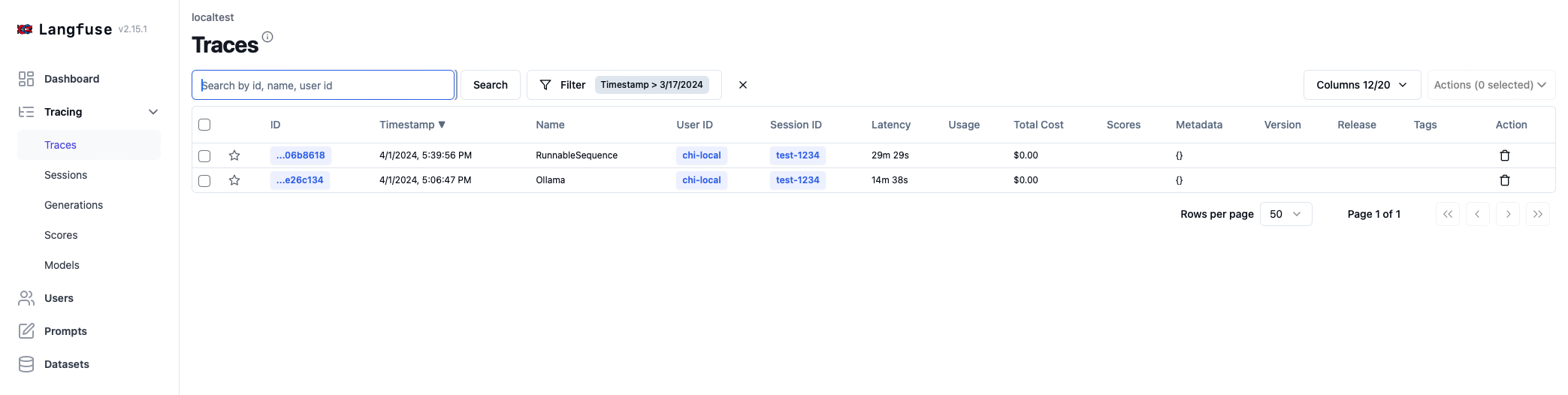
- And We’d be able to see this execution logged on Langfuse in Traces as we have setup the CallbackHandler. This supports us keep track of the input, output, latency, number of tokens, cost and more.
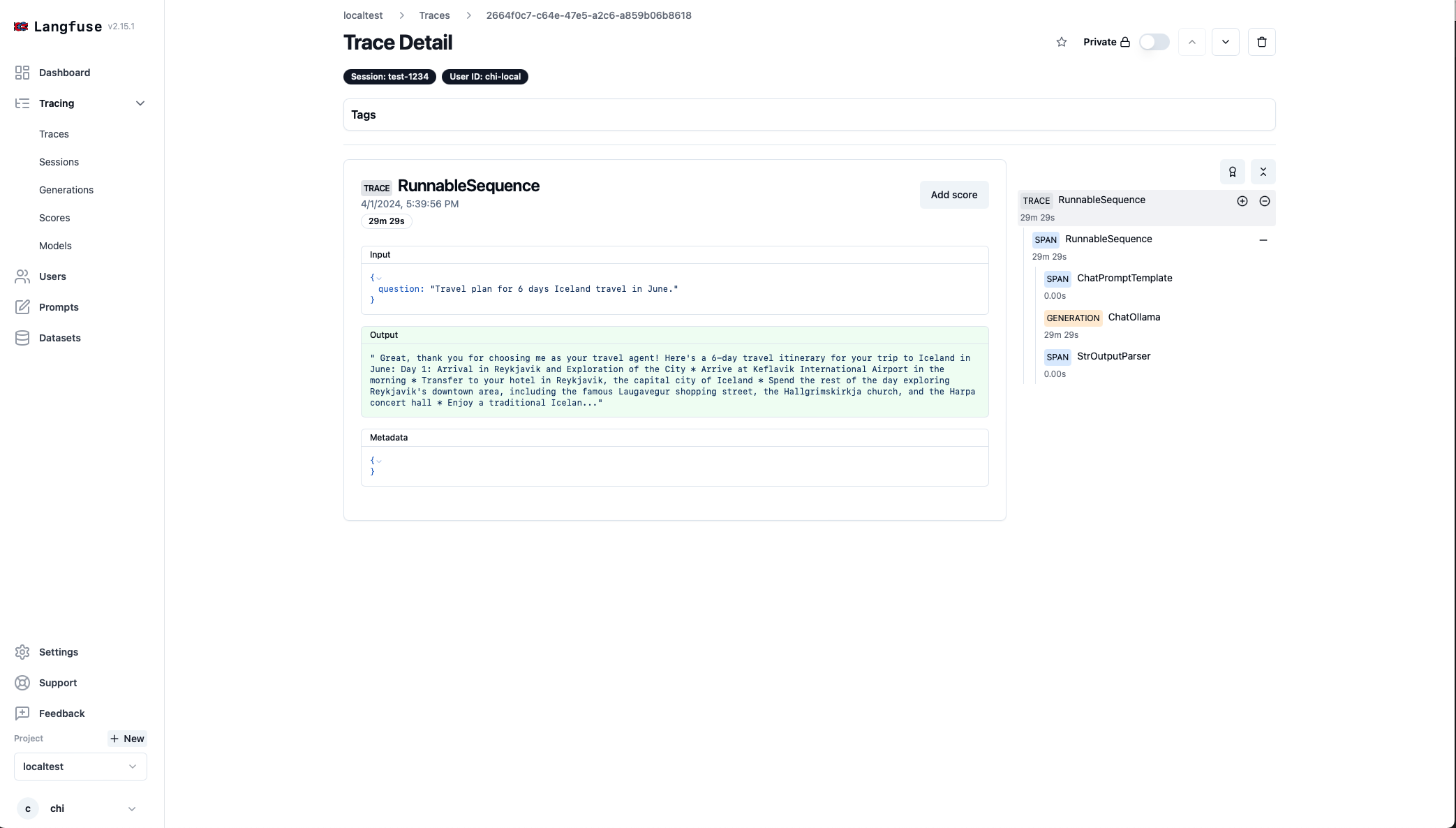
- Multiple executions under the same project can be tracked, which can used as a dashboard to support debugging for data scientists.